Digital Traceability Events
Please note that this content is under development and is not ready for implementation. This status message will be updated as content development progresses.
Artifacts
Are maintained at https://test.uncefact.org/vocabulary/untp/dte/0/about
Stable Releases For Implementation
Version 1.0 stable release for production implementation is due in June 2025 after formal public review
Release for Pilot Testing
Version 0.6.0 release artifacts can be used for pilot testing.
Latest Development Version
Latest development versions are used to reflect lessons learned from pilots but should not be used for either pilot testing or production purposes.
Ontology
The ontology for Digital Traceability Events is available in JSON-LD format and can be retrieved via content negotiation from:
https://test.uncefact.org/vocabulary/untp/dte/0/
Example:
curl https://test.uncefact.org/vocabulary/untp/dte/0/ -H 'Accept: application/ld+json'
Version History
History of releases is available from the Version history page.
Visualization
A UNTP digital traceability event may be rendered in any format desired by the issuer. However a default Visualization is provided here and includes mapping of visual rendering elements to the Logical Data Model.
Sample Credential
| URL | QR | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Battery Transformation Event |  | A sample digital traceability event (transformation) as a JWT envelope signed Verifiable Credential. The URL (or QR scan) resolved to a hosted verifier that displays a human readable version. Raw JSON data can be viewed via the JSON tab and the full credential can be downloaded via the download button. |
Overview
Traceability events are very lightweights collections of identifiers that specify the “what, when, where, why and how” of the products and facilities that constitute a value chain. The UNTP leverages ISO/IEC 19987 standard for this purpose because it is an existing and proven mechanism for supply chain traceability. The basic idea behind the traceability event structure is that any supply chain of any complexity can always be accurately modeled using a combination of four basic event types. An object event describes an action on specific product(s) such as an inspection. A transaction event describes the exchange of product(s) between two actors such as sale of goods between seller and buyer. An aggregation event describes the consolidation or de-consolidation of products such as stacking bales of cotton on a pallet for transportation. An association event describes the assembly of sub-components to make a composite product. Finally, a transformation event describes a manufacturing process that consumes input product(s) to create new output product(s). The UNTP uses these events in a decentralised architecture as the means to traverse the linked-data "graph" that represents the entire value-chain.
Conceptual Model
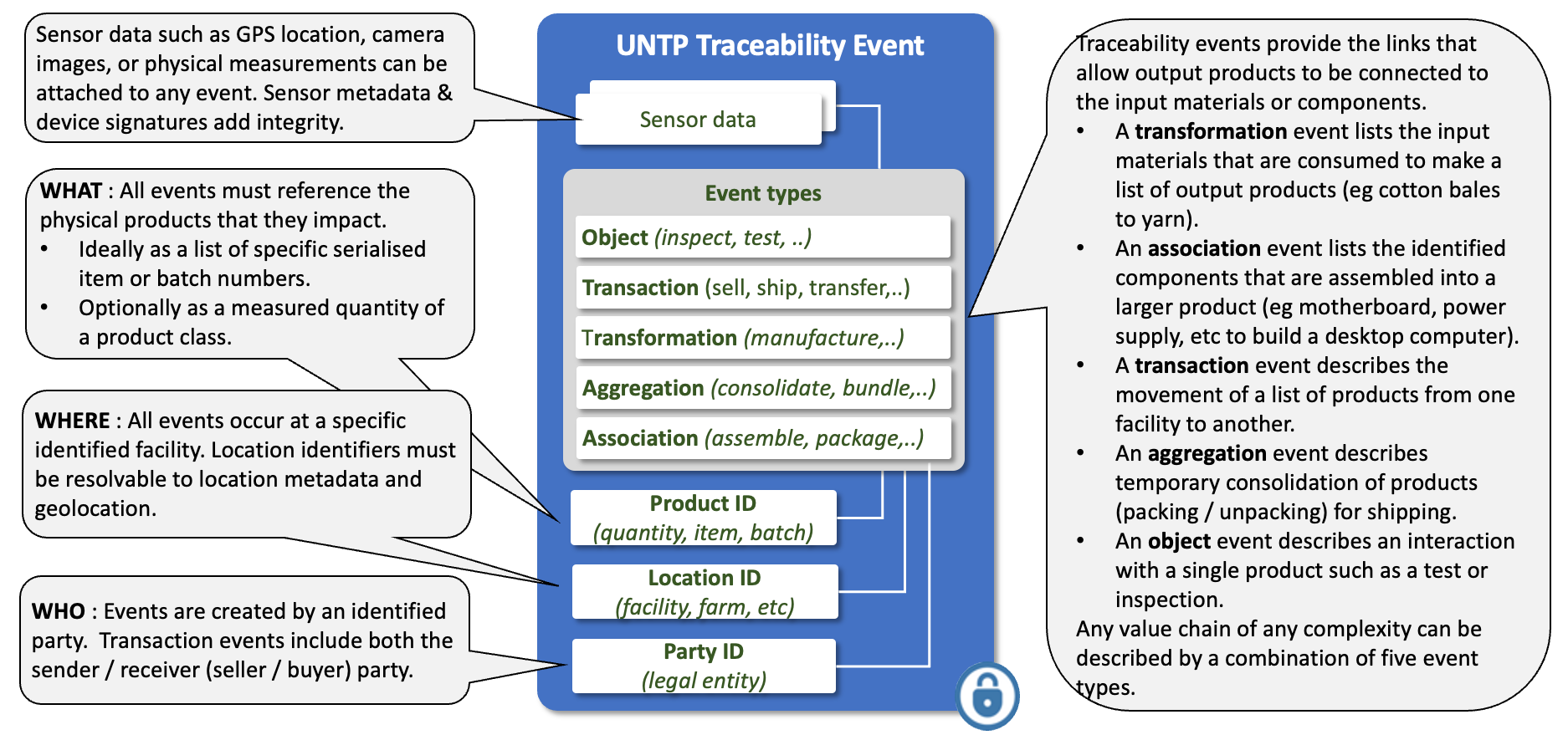
Requirements
The traceability event is designed to meet the following detailed requirements as well as the more general UNTP Requirements
| ID | Name | Requirement Statement | Solution Mapping |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEV-01 | Sub-components | The traceability event MUST provide a mechanism to trace from a DPP representing a product assembly to the individual DPPs of each sub-assembly component part | Association Event |
| TEV-02 | Consumed materials | The traceability event MUST provide a mechanism to trace a manufactured product DPP back to the DPPs representing batches of input materials that are consumed in manufacturing one or more output products. | Transformation Event |
| TEV-03 | Aggregated bundles | When a DPP represents an aggregated bundle of similar items (eg a pallet of cotton bales) then the traceability event MUST provide a means to allocate the aggregate measures to each individual item (ie each bale) | Aggregation Event |
| TEV-04 | Transportation | when a product (or consolidated consignment) is shipped from one physical location to another, the traceability event MUST provide a means to record the movement and associate sustainability measures such as transport emissions to the shipped bundle | Transaction event |
| TEV-05 | items or quantities | Traceability events MUST work equally well whether the input or output items are individually serialised items or measured quantities (mass or volume) of a product class. | Items Quantity |
| TEV-06 | IoT Sensor data | Traceability events will often be generated by or associated with physical sensor readings. In such cases, the traceability event SHOULD support the association of sensor data with the event | Sensor element |
| TEV-07 | Time & Location | Traceability events MUST always record the timestamp and physical location of the event so that multiple events can be be connected in time and space | Event |
Logical Model
Core Vocabulary Documentation
The UNTP core types vocabulary defines the uniquely identified Linked Data entities such as Product, Location, Facility, Party, Standard, Regulation, Criteria, Declaration, Attestation, Endorsement. These entities provide the building blocks for construction of Digital Product Passports and Digital Conformity Credentials.
DTE Documentation
The UNTP Digital Traceability Events Vocabulary defines the core traceability event and its variants including aggregation event, transformation event, association event, transaction event, and object event.
Implementation Guidance
Verifiable Credential
Digital Traceability Events are issued as W3C Verifiable Credentials. Note that one UNTP Digital Traceability Event credential may contain multiple events.
Please refer to DPP VC Guidance for information about the use of the verifiable credentials data model for UNTP.
Traceability Event
There are five types of traceability event which all extend the same abstract Event model.
- A
TransformationEventdescribes manufacturing processes where input materials are consumed and/or assembled to create new output products. For example cotton thread is consumed to make woven cotton fabric. - An
AssociationEventis used to establish relationships between otherwise independent items. For example new tyres on a car. - An
AggregationEventdescribes the grouping (or un-grouping) of a quantity of similar items, usually for transport. For example the stacking of several bales of cotton onto a pallet. - A
TransactionEventrepresents the transfer of products between organisations or facilities. For example the sale of some cotton cloth from seller to buyer. - An
ObjectEventrepresents an action on an individual item or quantity of product. For example an inspection or test of a battery.
Any value chain of any complexity can be represented as a combination of these types of events. However for UNTP value chain traceability, the most important event is the transformation event because it represents a manufacturing step that consumes inputs to create new outputs. When an identified output product (with its digital product passport) can be traced to its identified input products (each with their own digital product passport) then a linked set of credentials can be followed to define an entire value chain.
Transformation Event
This transformation event example describes the manufacture of a battery cell (output EPC) from an anode and a cathode (input EPC list) and a quantity of electrolyte (input quantity list).
"credentialSubject": [
{
"type": [
"TransformationEvent",
"Event"
],
"id": "https://events.sample.com/b681df10-c682-454a-b11b-d0b9374c01bd",
"processType": "Cell Manufacture",
"eventTime": "2024-09-01T12:00:00Z",
"action": "add",
"disposition": "active",
"bizStep": "commissioning",
"bizLocation": "https://plus.codes/8CGRC78W+MM",
"sensorElementList": [...],
"outputEPCList": [
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/12345",
"name": "EV battery 300Ah."
}
],
"inputEPCList": [
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/99876",
"name": "Graphite Anode"
},
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/99987",
"name": "Copper Cathode"
}
],
"inputQuantityList": [
{
"productId": "https://id.sample.org/01/095201299876",
"productName": "Lithium electrolyte",
"quantity": 2,
"uom": "KGM"
}
],
"outputQuantityList": [...]
}
]
Association Event
This association event example describes the replacement of a new battery cell (child EPC) in an electric vehicle (parent EPC).
"credentialSubject": [
{
"type": [
"AssociationEvent",
"Event"
],
"id": "https://events.sample.com/b681df10-c682-454a-b11b-d0b9374c01bd",
"processType": "Replace battery",
"eventTime": "2024-09-01T12:00:00Z",
"action": "add",
"disposition": "active",
"bizStep": "commissioning",
"bizLocation": "https://plus.codes/8CGRC78W+MM",
"sensorElementList": [...],
"parentEPC": {
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://sample-car-company/VIN-Number/12345678987654",
"name": "My Electric car."
},
"childEPCs": [
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/12345",
"name": "EV battery 3000Ah."
}
],
"childQuantityList": [...]
}
]
Aggregation Event
This aggregation event describes the packaging for shipment of two battery cells (child EPCs) into a battery consignment (parent EPC)
"credentialSubject": [
{
"type": [
"AggregationEvent",
"Event"
],
"id": "https://events.sample.com/b681df10-c682-454a-b11b-d0b9374c01bd",
"processType": "Packing",
"eventTime": "2024-09-01T12:00:00Z",
"action": "add",
"disposition": "active",
"bizStep": "commissioning",
"bizLocation": "https://id.sample.org/414/9520123456788",
"sensorElementList": [...],
"parentEPC": {
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://consignments.com/1234567890",
"name": "shipment of batteries"
},
"childEPCs": [
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/12345",
"name": "EV battery 300Ah."
},
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/678910",
"name": "EV battery 300Ah."
}
],
"childQuantityList": [...]
}
]
Transaction Event
This transaction event describes the sale of 200 batteries (quantity list) from source party to destination party.
"credentialSubject": [
{
"type": [
"TransactionEvent",
"Event"
],
"id": "https://events.sample.com/b681df10-c682-454a-b11b-d0b9374c01bd",
"processType": "Shipping",
"eventTime": "2024-09-01T12:00:00Z",
"action": "add",
"disposition": "active",
"bizStep": "commissioning",
"bizLocation": "https://plus.codes/8CGRC78W+MM",
"sensorElementList": [...],
"sourceParty": "https://somebusinessregister/ID/9988765443",
"destinationParty": "https://abr.business.gov.au/ABN/View?abn=90664869327",
"bizTransaction": "prodorder",
"epcList": [...],
"quantityList": [
{
"productId": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788",
"productName": "EV battery 300Ah.",
"quantity": 200,
"uom": "KGM"
}
]
}
]
Object Event
This object event describes the repair of a battery cell (EPC list).
"credentialSubject": [
{
"type": [
"ObjectEvent",
"Event"
],
"id": "https://events.sample.com/b681df10-c682-454a-b11b-d0b9374c01bd",
"processType": "Repair",
"eventTime": "2024-09-01T12:00:00Z",
"action": "add",
"disposition": "active",
"bizStep": "commissioning",
"bizLocation": "https://id.sample.org/414/9520123456788",
"sensorElementList": [...],
"epcList": [
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/12345",
"name": "EV battery 300Ah."
}
],
"quantityList": [...]
}
]
Item
The item structure is designed to represent serialised items such as a specific battery cell.
"outputEPCList": [
{
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://id.sample.org/01/09520123456788/21/12345",
"name": "EV battery 300Ah."
}
]
Quantity Element
The quantity element structure is designed to represent a measured quantity such as 20kgs of lithium hydroxide.
"inputQuantityList": [
{
"productId": "https://sampleRegister.com/material/876544321",
"productName": "Lithium hydroxide",
"quantity": 20,
"uom": "KGM"
}
]
Sensor Element
The sensor element structure accommodates the association of one or more sensor readings to a given event. Each reading is measured by an identified sensor.
"sensorElementList": [
{
"sensorMetadata": {
"device": {
"type": [
"Item"
],
"id": "https://sampledeviceregister.com/123456",
"name": "Temperature sensor",
},
"dataProcessingMethod": "https://standards.org/sensorMethod#1234"
},
"sensorReport": [
{
"time": "2024-07-24T12:00:00Z",
"sensorType": "https://samplesensors.com/model1234",
"value": 25,
"uom": "KGM"
},
{
"time": "2024-07-24T12:00:00",
"sensorType": "https://samplesensors.com/model1234",
"value": 25,
"uom": "KGM"
}
],
"sensorIntegrityProof": "..."
}
]

